How Does UV LED Area Curing Differ From Traditional UV Lamp?
A Guide to Understanding the Difference
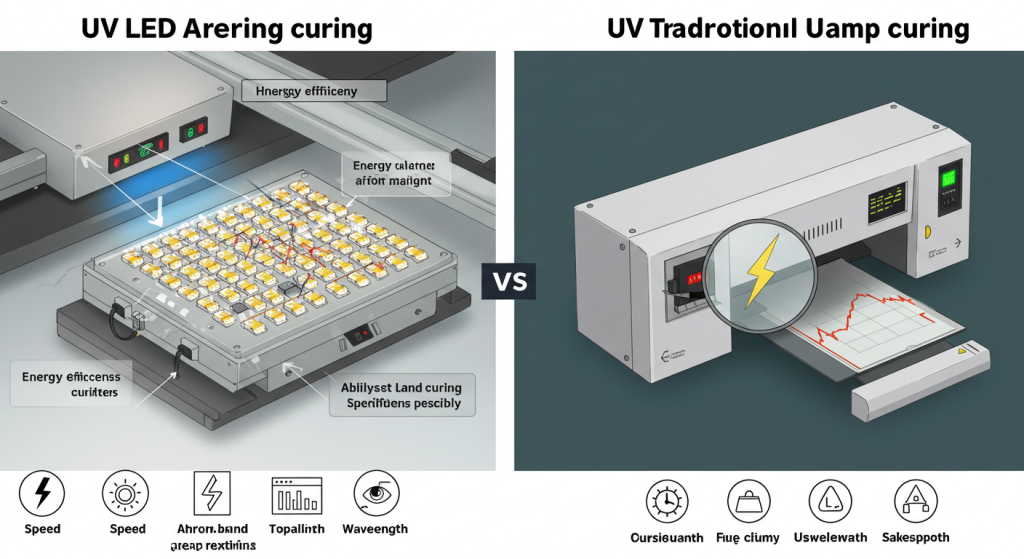
How does UV LED area curing differ from traditional UV lamp? The difference between traditional UV lamps and area LED systems cannot be understated. For manufacturers, engineers, and company decision-makers looking for speed, sustainability, and lower costs, these two technologies present vastly different capabilities. Join us as we analyze the most important distinguishing features of UV LED area curing.
Comparing Basics: Traditional UV Lamp and UV LED
The use of traditional UV mercury or arc lamps spans several decades. Their application in industrial printing, coating, and adhesive curing is well known. Both types of lamps used in these processes have their specific advantages as they provide high-temperature UVA, UVB, and UVC rays in broad-spectrum output.
More modern solid-state light sources enable UV LED area curing. Unlike traditional UV lamps, these systems emit narrowband focused UV light at specific wavelengths 365nm, 385nm, 395nm, or 405nm. This increases the efficiency of curing control and reduces damage to the substrates.
Differences in the Emissions and Wavelengths
It’s easy to see the difference in emission and wavelength with UV LEDs. While traditional UV lamps emit a broad spectrum of UV radiation, UV LEDs only emit light at the desired wavelength and do so with great precision. This is beneficial as it ensures that the photoinitiators are responsive for efficient polymerization in the coatings and adhesives.
Differences in Heat Generation and Substrate Compatibility
The most prominent differences are in heat generation and substrate compatibility. Traditional UV lamps emit a significant amount of infrared radiation, which not only affects the curing system but also the substrate. For some materials, especially those that are heat sensitive, this can cause damage.
In contrast, UV LED systems are cold light sources. Their minimal heat output permits cold curing, making them suitable for thin plastics and films as well as low-tolerance electronics.
Sustainability and Economic Application of Power
Unlike UV LEDs, traditional mercury lamps consume power. Additionally, they need to be warmed up, and they tend to remain in in-between production cycles to be 'performance ready.'
With the ability to turn off and on instantly, UV LED area curing systems have a marked advantage. Their minimal power consumption leads to a reduction in operational expenses while greatly improving energy efficiency. Studies indicate that power consumption can decrease by up to seventy percent with UV LED systems.
Curing Speed and Production Efficiency
In manufacturing, time is of the essence. With their narrowband, high-intensity output, UV LED systems have faster curing times, improving throughput and reducing bottleneck processes.
Area curing applications have always struggled with throughput due to traditional UV lamps needing longer exposure times and inconsistent irradiance.
Maintenance and Lifespan
UV mercury lamps require extensive maintenance due to bulb replacements. Traditionally, these lamps last only 1,000 to 2,000 hours.
UV LED arrays shine in this regard. They last over 20,000 hours, outperform mercury systems, and require fewer maintenance replacements, which results in lower UV curing maintenance costs.
Environmental Impact
Mercury UV lamps are hazardous due to the mercury they contain and need regulated disposal. Also, the short-wavelength emissions produce ozone, which is another environmental concern.
These UV LED systems are free from mercury and ozone creation. This assists in sustainable UV curing and helps companies meet green compliance.
Curing Chemistry and Photoinitiators
Different light sources utilize different types of photoinitiators, which impact the resultant LED reaction and its precision. Within LED curing, photoinitiators intended for narrowband illumination are used.
Broad-spectrum UV emission from mercury lamps often leads to inefficient curing because it does not have photoinitiator absorption maxima. This can negatively impact the curing speed or quality.
System Footprint and Integration
Traditional UV systems need considerable space for housing and require cooling fans and ventilation due to ozone and heat emissions. This adds to the overall footprint of the devices.
UV LED systems have a compact construction and modular design. Their smaller footprint facilitates integration into automated production lines, which makes them fit for modern industry.
Process Control and Irradiance Uniformity
The precision control of irradiance, intensity, and wavelength makes UV LED area curing systems unrivaled in terms of uniformity and coverage in large-area curing.
Traditional UV arc lamps are less reliable when it comes to process control due to the intermittent hot spot fluctuating output during the UV curing process.
Applications: From Printing to Electronics
• Printing UV curing: Instant drying with UV LED systems on paper, plastic, and metal.
• Medical-grade formulations: Effective curing of optically clear adhesives (OCA), and structural adhesives.
• Coating curing: In automotive, wood, as well as industrial coatings.
• 3D Printing UV LED: UV LEDs are suited for the post-curing of resin models in 3D printing.
Cost Considerations: Upfront vs Long-Term
Although UV LED systems are more expensive to acquire, they have a better ROI. Cost-effective UV curing options arise from their long lifespan, energy savings, and low maintenance.
The traditional UV systems are cheaper to purchase at first. However, ongoing expenses for replacement bulbs, system downtime, and energy usage far outweigh the initial savings.
Safety Considerations
Safety is always the priority. Conventional UV lamps pose a health risk because they emit ozone along with excessive heat. They require protective equipment, and proper workspace ventilation is a must.
All these concerns are eliminated with UV LED curing systems. Their cool operation and mercury-free design make them safer for the operators and the environment.
Future of UV Curing: The LED Advantage
Modern UV curing technology is the focus. In response to industry demands for faster, greener, and safer solutions, UV LED systems are quickly becoming the preferred solution. They are perfect for companies looking to replace outdated UV curing systems, cut back on expenses, and adopt eco-friendly approaches.
Conclusions
How does UV LED area curing differ from traditional UV lamp? It is the safety, the focus, the effectiveness, and the eco-friendliness. UV LED systems are far more advanced—using less energy, producing less heat, and offering greater curing control. For more details on the shift towards UV LED systems, visit UVET UV LED solutions.