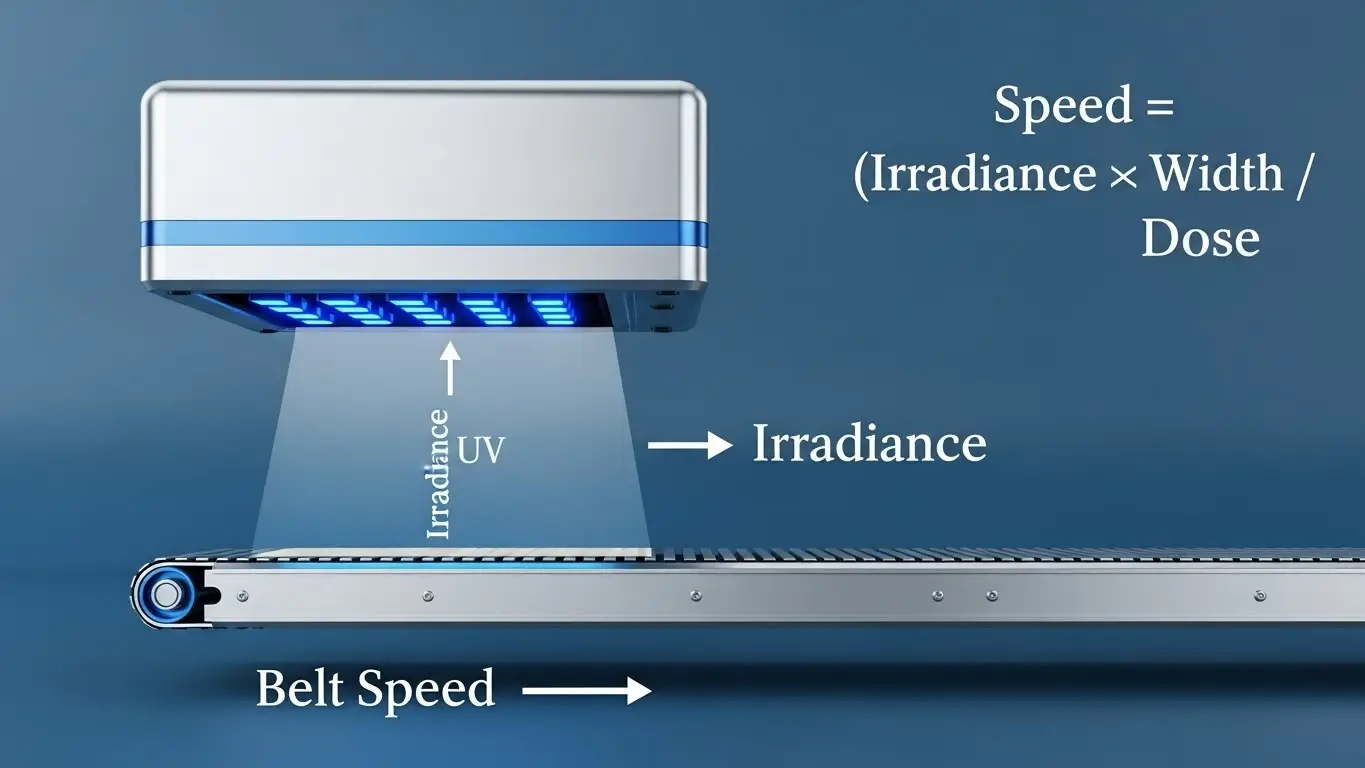
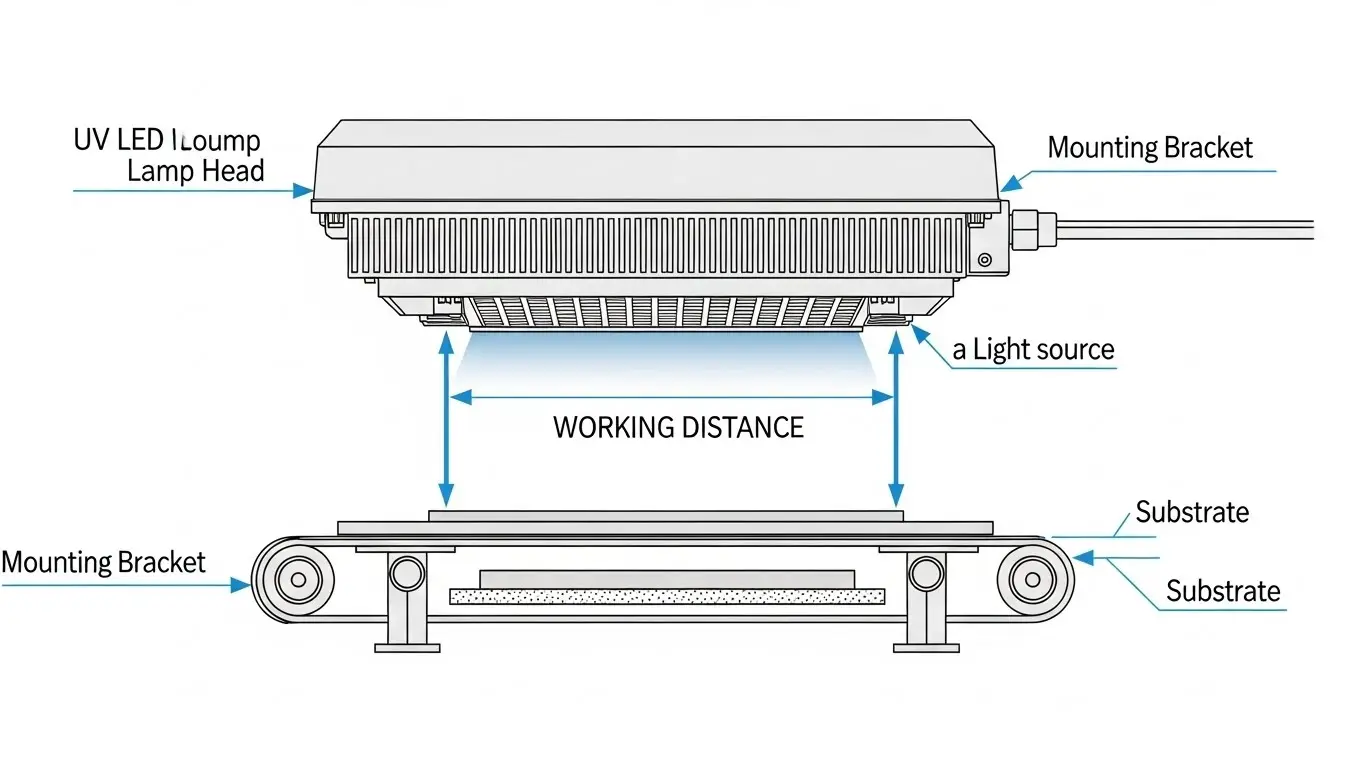
How Does UV LED Curing Work? A Guide to Photopolymerization
How Does UV LED Curing Work? Uses of UV LED Curing Solutions
If you work in printing, 3D manufacturing, or electronics, knowing how UV LED curing works will ensure you make the most out of your tools. Industries are being shifted towards the use of UV LED curing solutions due to their being cleaner, more energy efficient, and faster than traditional curing methods. This blog describes how does UV LED curing work?
What is Curing With UV LEDs?
Curing in LED UV light refers to the application of light from diodes to ultraviolet UV curing by UV LED. This entails starting a chemical reaction that hardens inks or coating materials, meaning that adhesives also go through changes, solidifying. This method is popular for the environmental advantages it gives as well as its speed and precision.
How Does Curing With UV LEDs Work?
The application of LEDs additionally serves to broaden the scope of ‘ light curing’ since Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) can be used to generate UV light. Curing (hardening or drying) of inks, coatings, adhesives, and resins is instantly done by exposing them to Ultraviolet light from LED sources D. Unlike traditional mercury lamps, UV LEDs are tailored to activate photoinitiators in UV-curable materials.
- This process starts with photoinitiators, molecules present in the material that absorb UV light. These molecules, once exposed to the appropriate UV wavelength, undergo cleavage and initiate photopolymerization, which is the process of creating solid, cross-linked polymers from monomers and oligomers, forming lasting surfaces. This step creates a tough surface that can dry almost instantly, within seconds.
- Curing with UV LED light has multiple benefits: it is more energy-efficient and does not have mercury in it, it is at a lower temperature than other methods, and is hence better for sensitive substrates like plastics or thin films. It also enhances the speed of production, the durability of the parts produced, and lowers the carbon footprint of the process.
- From industrial-scale printing and assembly of electronics to the production of automotive components, 3D printing, and even medical devices, the applications are endless. This technology makes it possible to achieve speed and precision, which makes it ideal for modern-day manufacturing.
Mechanics of UV LED Curing
1. Photopolymerization
The heart of photo polymerization makes the UV LED curing device work. The photoinitiators, which are light-sensitive, are capable of absorbing UV light and producing extremely reactive species capable of starting polymerization. In doing so, the liquid monomers and oligomers present are converted into solid polymers.
2. Role of Photoinitiators
Particular focuses in the field of polymer photoinitiators are driving forces in UV curing and require a lot of attention. To initiate the process of polymerization, defining UV light is essential, as it captures the light and produces either free radicals or cations. The photoinitiator opt region, the UV light wavelength used and the application required will impact the choice.
3. Cross-Linking
The entire process of curing is a monomer and oligomer cross-linking, chains or links with cross-overlap create a three-dimensional structure known as a polymer network. This cross-linking is what gives strength, durability, and enhancement of resistance to the material that has been cured.
4. UV LED Technology
Unlike conventional mercury lamps, UV LED lamps are considered economical as they conserve energy, have an elongated lifespan, and emit less heat. Furthermore, UV LEDs, which are required for curing, can emit light of specific wavelengths such as 365nm, 385nm, 395nm, 405nm, and even 405.
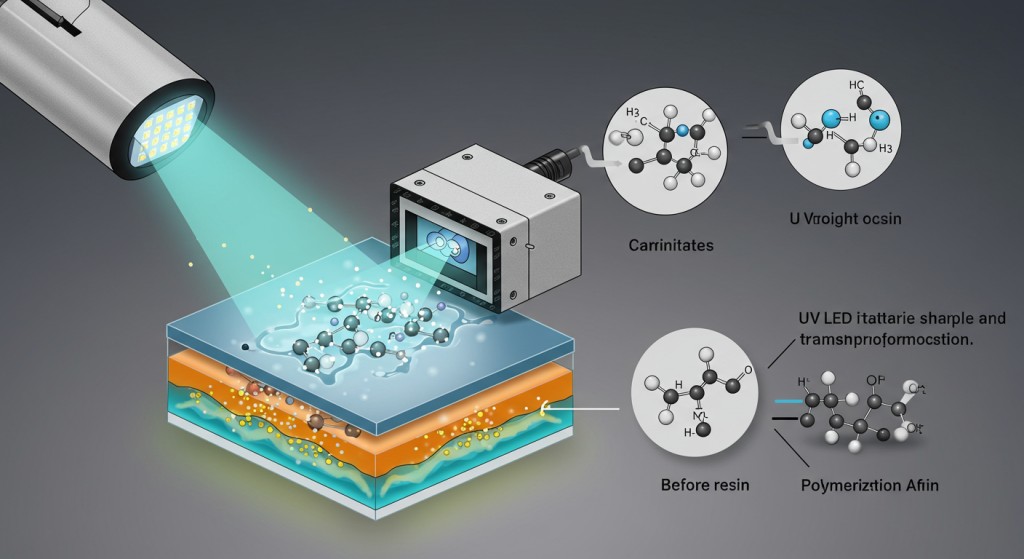
Advantages of UV LED Curing
1. Curing Times are Faster
The speed at which light waves are processed is very rapid in curing processes, which increases the speed and efficiency of production.
2. Energy Efficiency
Because of the lower power consumption, UV LEDs offer substantial energy savings.
3. Cooler Temperatures
The low thermal radiation permits the curing of substrates sensitive to heat without damaging the substrate.
4. Longer Lifespan
The lifespan of an LED is much greater than a lamp UV, which means lower servicing expenses for the system.
5. Environment-Friendly
Because there is no mercury and no ozone is produced, it is more eco-friendly to
Maintaining UV LED Efficiency During Curing
Certain factors dictate the amount of attention and management required to fully utilize the advantages offered by UV LED curing systems. One of these factors is the thermal regulation at the core of the UV LED system. Thermal management is key to the continued operational life and reliability of the diodes. To maintain performance levels, manufacturers use advanced cooling apparatuses to control heat flow. Understanding the process window as specified by a material and application is equally important. The process window refers to the minimal and maximal values of energy density and peak irradiance, which, if not followed, will lead to incomplete and fractured features. Achieving complete curing is only possible through careful calibration of numerous parameters to ensure balanced material properties.
The Move to Curing with UV LEDs
The motivation behind the continuously widening gap between laser and conventional curing systems is the list of advantages provided on performance, effectiveness, and environment.
UV LEDs are changing the game when it comes to controlled lighting systems. LED systems boast numerous features when compared to other curing technologies, including:
Reduction of Time Spent on Curing Materials:
This is one of the more captivating benefits as it warrants technologically enhanced methods of production. Compared to non-LED cured systems, LED-cured systems process components in milliseconds, leading to greater productivity.
Cooler Temperatures:
Curing using UV LEDs is much less thermally intensive since it produces minimal infrared (IR) heat. This is a breakthrough for heat-sensitive materials such as thin films, some plastics, and certain electronics as they would deform or degrade due to the extreme heat emitted by conventional UV lamps.
Longer Lifespan (UV LEDs):
Compared to mercury arc lamps with a lifetime of a few thousand hours, UV LED lamps have tens of thousands of hours. This extends maintenance downtime, reduces costs in lamp replacements, and decreases the frequency of recalibrations needed.
Conclusion
How does UV LED curing work? UV LED curing is a fast, clean, and energy-efficient solution for industries requiring high-performance bonding, printing, or coating. Its cold-curing, instant-on capability, and long lifespan make it ideal for sensitive components in electronics, medical devices, optics, and beyond. As technology advances, UV LED curing continues to replace older methods, bringing innovation, sustainability, and enhanced productivity to modern manufacturing processes.