UV LED vs Mercury UV Curing: Differences, Pros, Cons & ROI
Evaluating UV LED vs mercury UV curing is a critical step in optimizing your industrial manufacturing process. You will find that these two technologies represent very different approaches to delivering ultraviolet energy to your inks, coatings, and adhesives. While traditional mercury lamps have served the industry for decades, LED technology has introduced new variables in energy use, heat management, and maintenance cycles. This guide provides you with a technical comparison of both methods to help you understand the operational trade-offs and the long-term economic impact on your production line.

What Are the Key Differences Between UV LED and Mercury UV Curing?
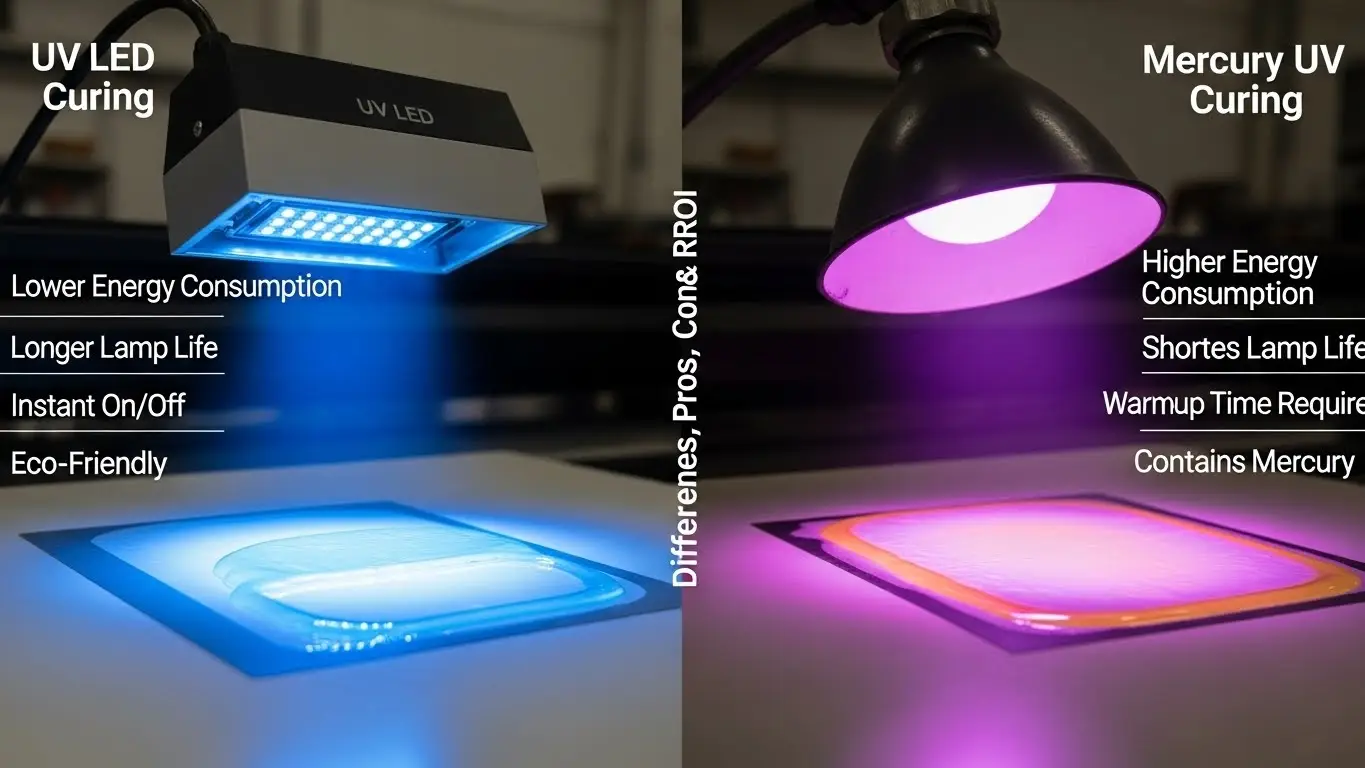
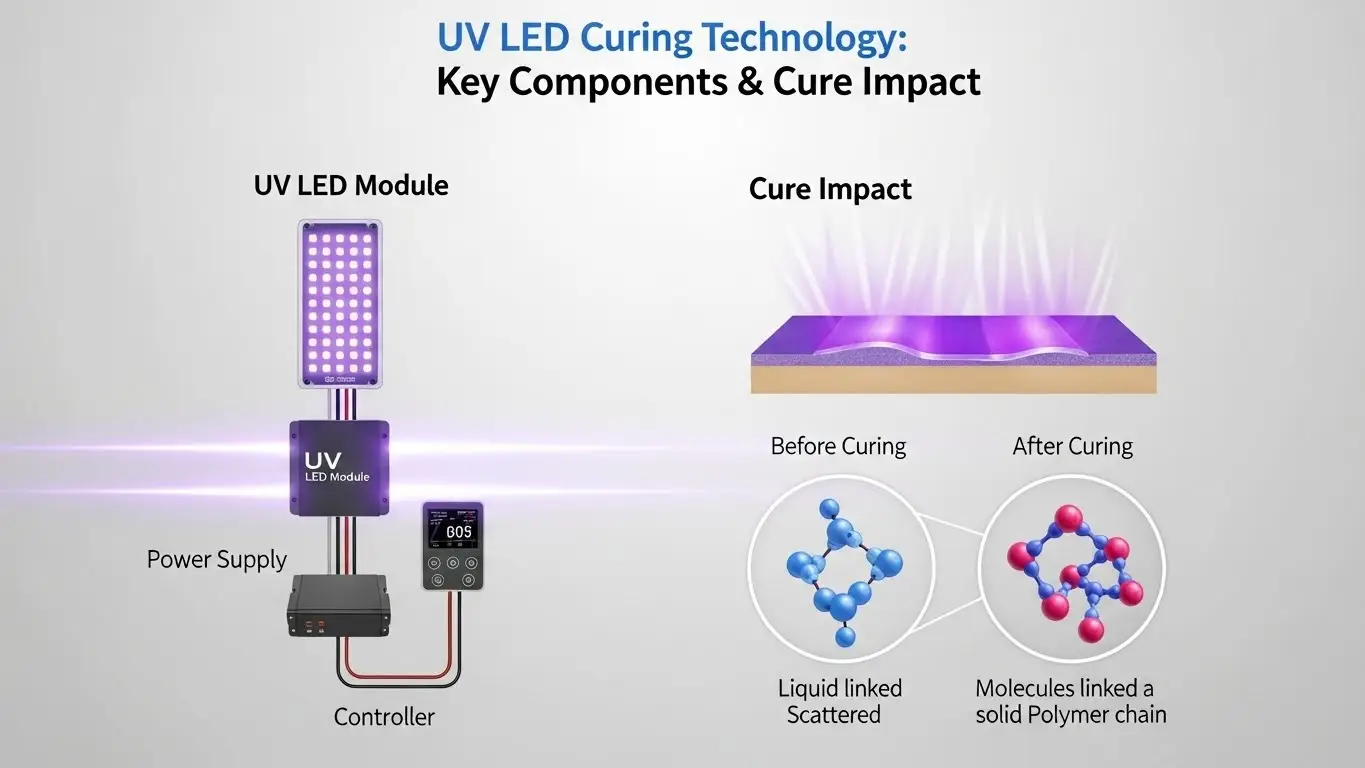
UV LED and mercury UV curing differ in light generation, energy delivery, and operational characteristics. You use mercury lamps to produce a broad spectrum of ultraviolet light through a high-pressure gas arc, which also generates significant infrared heat and ozone. In contrast, you use UV LED systems to emit a narrow, targeted band of light through solid-state semiconductors. This fundamental shift in how the light is created means that your mercury system requires warm-up times and extensive cooling, while your LED system provides instant power and operates at much lower temperatures.
The physical design also impacts your workspace. Mercury lamps require large ballasts and complex ductwork to remove heat and ozone from the building. Your LED setup is typically more compact, allowing you to mount it in tight spaces on your conveyor or robotic arm. Because the LED wavelength is concentrated, you get a more efficient transfer of energy to the specific photoinitiators in your coating, whereas mercury light is spread across a wider spectrum, much of which may not be needed for your specific cure.
What Are the Pros of UV LED Curing Compared to Mercury UV?
UV LED curing offers specific operational advantages in many industrial environments, particularly regarding energy efficiency and material safety. You benefit from a light source that produces almost no infrared heat, allowing you to cure coatings on thin plastics or delicate electronics without risking thermal damage.
- Instant On/Off: You eliminate the 15-minute warm-up and cool-down cycles required by traditional bulbs, increasing your daily uptime.
- Lower Power Consumption: You only use electricity when the LEDs are actively curing a part, often reducing energy use by over 50%.
- Long Lamp Life: Your LED arrays can last for 20,000 to 30,000 hours, which is up to 20 times longer than mercury bulbs.
- Environmental Safety: You work with a mercury-free system that does not produce ozone, simplifying your facility's ventilation needs and meeting green standards.
What Are the Cons or Limitations of UV LED Curing Relative to Mercury UV?
UV LED curing has limitations that can affect its suitability in some applications, primarily concerning wavelength range and material chemistry. You may find that your existing inks or coatings do not react to the narrow-band light emitted by LEDs, requiring you to reformulate or purchase new, often more expensive, materials.
- Narrow Spectrum: Because LEDs emit only one peak wavelength, you might struggle to achieve a full surface cure on coatings designed for broad-spectrum mercury light.
- Higher Initial Cost: You will likely pay a higher upfront price for LED equipment compared to standard mercury lamp setups, which can be a hurdle for smaller budgets.
- Surface Cure Challenges: Without the UVC wavelengths found in mercury lamps, some of your coatings might remain tacky on the very top layer.
- Chemistry Dependence: You must ensure your photoinitiators are specifically tuned to the LED wavelength, or the chemical bond will fail to reach full strength.
What Are the Pros of Mercury UV Curing Compared to UV LED?
Mercury UV curing still has advantages in certain legacy and high-intensity use cases due to its broad spectral output. You can use a single mercury lamp to cure a wide variety of different inks and resins because it provides a "cocktail" of UVA, UVB, and UVC light. This versatility makes it a reliable choice if your shop handles many different types of jobs with varying chemical requirements.
- Broad Spectrum: You get deep penetration and excellent surface hardness across many material types with a single light source.
- Proven Technology: You are working with a system that has decades of established testing and material compatibility, making it easier to find off-the-shelf coatings.
- Lower Upfront Cost: You can often install a mercury system for a lower initial investment than a high-power LED array, which may be helpful for new businesses.
What Are the Practical Cons of Mercury UV Curing Compared to UV LED?
Mercury UV curing presents practical disadvantages relative to UV LED in many settings, specifically regarding heat, maintenance, and safety. You must manage a light source that operates at extremely high temperatures, which can warp your substrates and increase your air conditioning costs.
- High Maintenance: You must replace bulbs every 1,000 to 2,000 hours and clean reflectors frequently to maintain intensity.
- Safety Hazards: You have to deal with the risk of toxic mercury exposure if a bulb breaks and manage the ozone gas produced during operation.
- Energy Waste: Your lamps stay on even when no product is on the line because they cannot be turned on and off instantly.
- Bulb Degradation: You will notice a steady drop in UV output over the life of the bulb, making your process less predictable as the lamp ages.
How Should You Approach ROI When Comparing UV LED and Mercury UV Curing?
Evaluating ROI requires looking beyond upfront cost to long-term operational factors such as energy savings, maintenance labor, and production uptime. You should calculate your total cost of ownership by weighing the initial equipment price against the thousands of dollars you might save in power and replacement bulbs over several years.
- Energy Savings: Track how much electricity your current mercury lamps waste during warm-up and line pauses.
- Maintenance Uptime: Consider the cost of stopping your line every few months to change mercury bulbs and the labor involved in cleaning reflectors.
- Scrap Reduction: Factor in the lower rejection rates you get when using cool LED light on heat-sensitive materials that used to warp.
- Facility Impact: Evaluate the savings from removing expensive ozone exhaust systems and reducing the massive heat load in your production shop.
What Factors Should Influence Technology Choice in Your Process?
Technology choice depends on specific process criteria and priorities, such as your substrate's heat tolerance and your throughput goals. You should analyze your material's chemical requirements first to see if an LED-compatible version is available. If your products are made of thin films or heat-sensitive plastics, the low-heat benefit of LED may be your deciding factor regardless of the equipment cost.
- Substrate Sensitivity: Pick LED if your parts melt or warp under high heat.
- Material Availability: Verify that your ink or adhesive supplier offers an LED-curable option that meets your bond requirements.
- Production Volume: High-volume, continuous lines often see a much faster return on investment with LED technology.
- Safety Goals: If your company is pushing for a mercury-free or ozone-free environment for worker health, LED is the clear path.
What Are the Key Takeaways When Comparing UV LED and Mercury UV Curing?
Your technology choice should be based on an informed evaluation of your specific production needs rather than following general trends. You must balance the modern efficiency and safety of LED against the broad spectral versatility and lower initial cost of mercury.
- LED is superior for heat-sensitive parts and energy reduction.
- Mercury remains a strong choice for broad-spectrum chemistry and legacy materials.
- ROI is usually realized in the long term through lower maintenance and power costs.
- Material compatibility is the most important technical hurdle when switching to LED.
How Does UV LED Curing Work Compared to Mercury UV Curing?
The core physics of these two light sources determine how they interact with your materials. You can explore a deeper technical breakdown of these spectral differences by visiting our page on UV LED vs mercury UV curing. This will help you visualize how the wavelength output changes your final cure quality.
What Are the Specific Differences Between LED and UV Curing Lamps?
When you look at the hardware itself, the components vary significantly. You should compare the LED vs UV curing lamp architecture to see why one lasts much longer than the other. Understanding the internal design of the lamp heads helps you plan your maintenance schedules more accurately.
Can UV LED Replace Mercury UV Curing in Existing Processes?
If you are thinking about upgrading your current line, you need to know if a retrofit is possible. You can find guidance on whether UV LED can replace mercury UV curing and how to approach the retrofit process for your specific machinery.
What Influences the ROI of UV LED Curing Systems?
The math behind the switch is more than just energy bills. You can see a full breakdown of the factors that drive UV LED curing ROI to help you build a business case. This covers everything from bulb life to improved production speeds.
How Do Temperature and Heat Generation Differ Between UV LED and Mercury UV?
Managing the heat on your shop floor is a major part of your daily job. You should look at the specific data regarding UV LED curing temperature to see how much cooler your production area could be. This is especially important for maintaining the quality of thin or sensitive substrates.
What Are the Known Limitations of UV LED Curing Technology?
No technology is perfect for every task. You should be aware of the limitations of UV LED curing before you make a purchase. This allows you to plan your material formulations and line speeds around the technology's specific constraints.
How Do UV LED and Mercury UV Curing Compare in Safety Considerations?
Your operators' health is your highest priority. You can compare the safety profiles of both systems on our UV LED curing safety page. This explains how removing mercury and ozone changes your daily safety protocols and protective gear requirements.
What Criteria Should You Use to Compare UV LED vs Mercury UV Curing Systems?
When you are ready to make a final decision, a structured approach is best. We provide a guide to choose a UV LED curing system that includes a checklist of questions you should ask your equipment suppliers. This ensures you miss no technical details during your evaluation.
Final Thoughts
Selecting the right technology for your shop is about finding the balance between current needs and future goals. While mercury lamps offer a legacy of broad compatibility, the efficiency and safety of UV LED are becoming the new standard for modern manufacturing. You should focus on your material chemistry and your substrate's heat tolerance as your primary guides. By looking at the long-term ROI and the daily impact on your team, you can make a choice that improves both your quality and your bottom line. The right system is the one that allows you to produce the best possible product while keeping your operating costs as low as possible.
- PREV: test
- NEXT: Null