What Wavelength is Best for UV LED Curing? What You Need to Know
What Wavelength is Best for UV LED Curing?
As cured materials differ from each other, the best wavelength for UV LED curing also changes. What wavelength is best for UV LED curing? However, it is safe to assume that 365 nm, 385 nm, 395 nm, and 405 nm will cover most commercial and industrial applications.
- Wavelengths of 395 nm have dominated the industry and its fields due to being the most versatile and efficient. This is due to having good photoinitiators that make curing very fast with good depth penetration. This is ideal for curing inks, coating adhesives, and even optical fiber. It is preferred in a lot of manufacturing setups to maintain the balance between speed and depth.
- However, for thicker or pigmented materials, a 365 nm UV LED satisfying fill curing from top to bottom is more efficient. In fast surface curing, 405 nm UV LEDs excel and are great for fast-moving applications like cosmetics and consumer electronics.
Each UV wavelength has its pros, and that must be taken into consideration. The wavelength range of 365nm nm to 405nm must match the required application to achieve better objectives, such as lowering cost and boosting performance.
Process of Wavelengths and Photochemical Activation
UV LED curing can emit photochemical reactions in glues, coatings, and even inks with the use of UV light, adhesives, coatings, and inks. The most frequently used wavelengths in UV LED curing include:
- 365 nm: Deeply penetrates thick materials best.
- 385nm: Surface curing and penetration are equal.
- 395nm: Good depth with reasonably efficient curing.
- 405nm: Fast surfacing curing and rapid curing.
These wavelengths fall into the range of UVA (315-400 nm), which is widely utilized in ultraviolet curing systems because of its efficacy and safety.
Factors Affecting the Choice of Wavelength
1. Material Compatibility
Photoinitiators, materials, and their construction elements respond more readily to specific wavelengths. As an example, some adhesives and coatings are made to be cured under 365 nm light; however, other formulations may require 395 nm or 405 nm for better performance.
2. Curing Depth and Speed
Shorter wavelengths, like 365 nm, penetrate materials more, making them ideal for curing thick or opaque substances. On the other hand, longer wavelengths, like 405 nm, are absorbed more at the die surface. This results in faster surface curing.
3. Photoinitiator Absorption
Every photoinitiator has a particular set of absorption spectra. The absorption spectrum for a given photoinitiator differs from that of another photoinitiator and thus needs extensive research. Matching the UV LED wavelength to the photoinitiator peak absorption would make the best use of the energy supplied, with optimal curing for the system.

Uses of Particular Wavelengths in UV LED Systems
365nm UV LED Curing
Its main benefit is the ability to penetrate deeply into thick materials with a 365 nm wavelength. This also makes it useful when curing pigmented or filled materials, where deep energy penetration is required.
Because of its depth of cure, 365 nm UV LED curing is particularly useful in industrial coatings due to its strength and durability. It is also popular in part 3D printing for resins, where the strength and accuracy of the parts rely on proper curing. In addition, medical device manufacturers trust this wavelength for curing biocompatible and reliable adhesives because of the high demands for biocompatibility.
385 nm UV LED Curing
UV LED curing at 385 nm is a compromise and a hybrid between depth and speed. This wavelength is compatible with numerous types of materials as it provides efficient surface and subsurface curing. Its application is very common in electronics assembly, where component and coating curing at the highest precision is important for product functionality. Furthermore, 385 nm can be used for varnishes and coatings as these require uniformity and smooth surfaces. Dental materials also utilize this wavelength as rapid and reliable curing is performed without harm to delicate tissues.
395 nm UV LED Curing
The 395 nm wavelength is known for efficacious curing and is well known for the penetration-smooth speed balance. This can be achieved with numerous standard photoinitiators, so it can be used for many applications. This wavelength is often used for printing inks, where quick adhesion and drying are needed.
It is helpful for glass and plastics adhesives as it provides a strong bond with little curing time. Moreover, the 395 nm wavelength works well with curing optical fibre coatings, which are important for telecommunications regarding clarity and durability.
405 nm UV LED Curing
405 nm LED UV curing is highly effective for surface curing because of its speed. It is widely used in beauty, such as nail gels and cosmetics, giving smooth results in record time due to the fast and even curing. The consumer electronics industry also benefits from 405 nm curing for components and protective coatings, which allows for higher volume production.
Maximizing the Performance of UV LED Curing
For best results in LED UV curing, perform the following:
• Mismatch Wavelength with Material: Make sure the UV LED range satisfies the photoinitiator's absorbable wavelength apex.
• Thickness of Materials: Thicker materials need shorter wavelengths for complete curing.
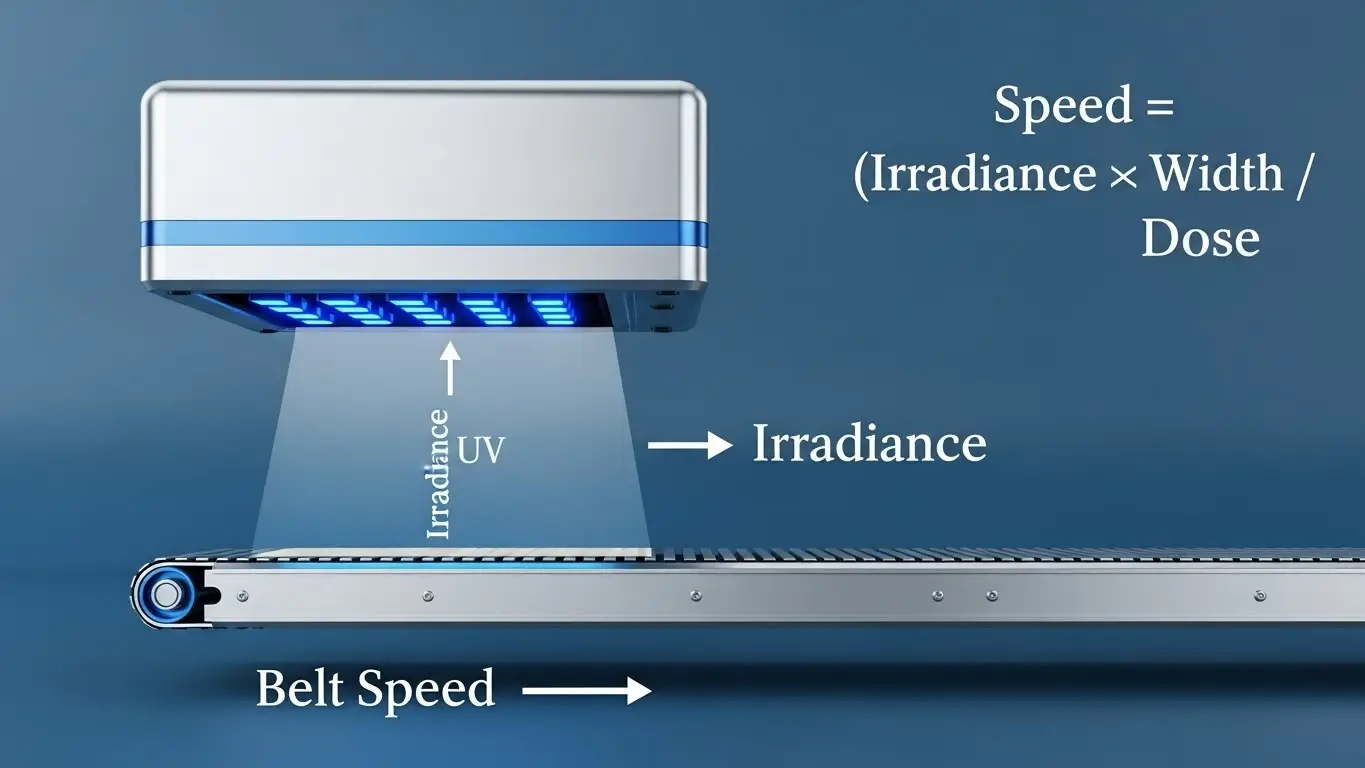
• Taper Irradiance: Set the level of UV light to either adjust the curing speed or avoid overheating.
• Control Curing Time: Cutlet M1 expression closure time to the achieved curing without negatively impacting the behaviours of material properties.
Conclusion
As noted, it is extremely important to select the optimal UV wavelength for LED curing processes, as it can affect overall efficiency, effectiveness, and the standard of the output. Visit UVET Technology for more information about UV LED curing technologies and applications. Improve defect detection and quality control with safe, efficient UV LED inspection methods. Get it today now!