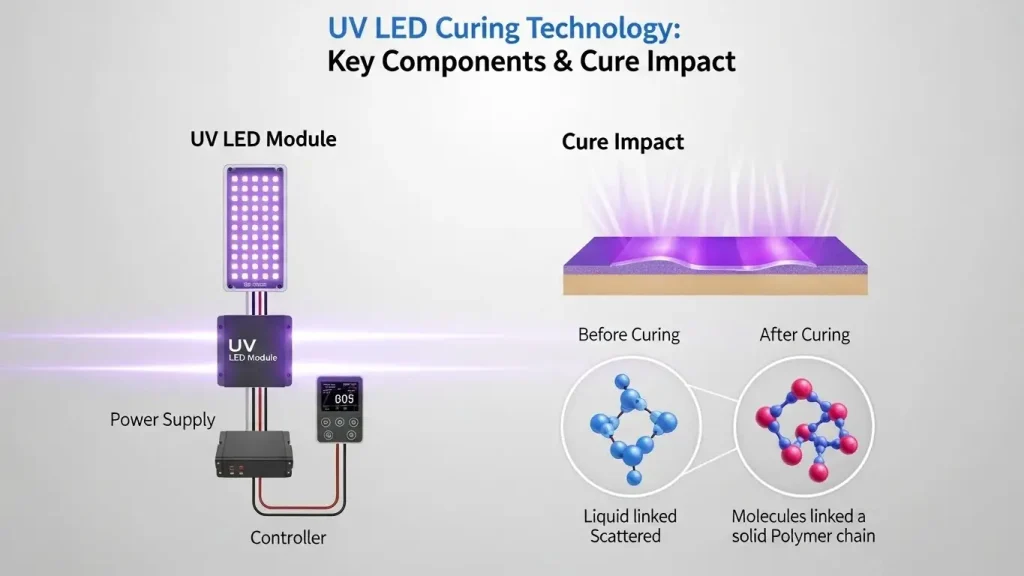
UV LED Curing Technology: Key Components and How They Affect Cure
Understanding UV LED curing technology requires you to look at the individual parts that make up the system and how they change your final product finish. You will find that the performance of your curing line depends on how well the emitters, optics, and power controls work together to deliver energy. This guide explains the essential building blocks of these systems and how each one influences the speed and quality of your process. By learning about these technical variables, you can better manage your production outcomes and ensure a reliable, long-lasting setup for your facility.
The shift toward light-emitting diodes in industrial manufacturing is driven by the need for more control. In older systems, you dealt with a broad spectrum of light that included heat and ozone. With modern technology, you can target specific chemical reactions with high precision. This focus not only improves the quality of your bond or coating but also reduces the physical stress on your machinery. As you explore the components below, keep in mind that the harmony between these parts is what creates a truly high-performance production environment.
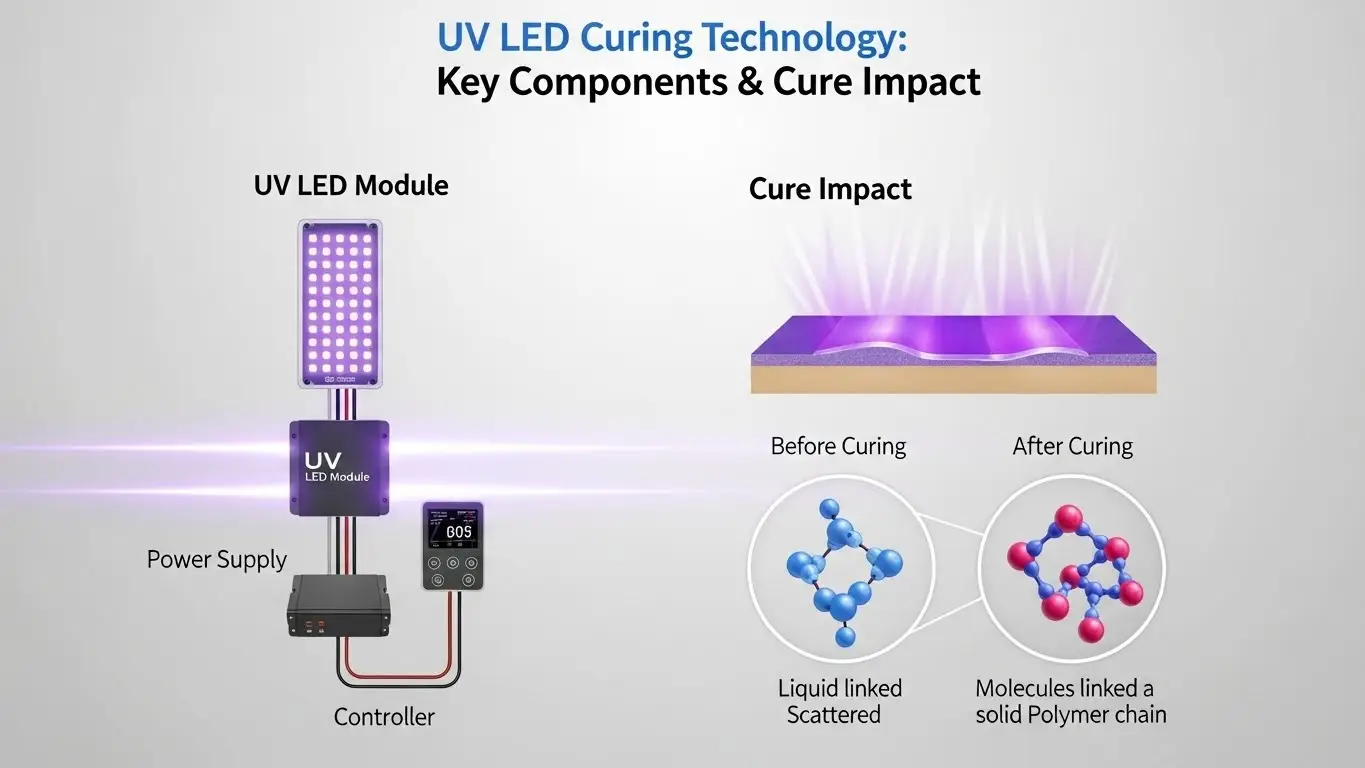
What Are the Key Components of UV LED Curing Technology?
The principal components of UV LED curing technology include the LED emitters, the optical system, the power supply, and the thermal management unit. You use these parts to generate, focus, and control the ultraviolet energy needed to harden your inks and coatings. Each piece plays a specific role in the system, and their coordination determines how effectively you can process your materials. By understanding these building blocks, you can better evaluate how a curing system will fit into your specific manufacturing workflow.
Beyond the core light engine, you must also consider the housing and the control interface. The housing protects the delicate electronics from the harsh environment of a factory floor, such as dust, ink mist, or vibration. The control interface allows you to communicate with the system, making adjustments based on real-time data from your production line. When these components are high-quality and well-integrated, you get a system that operates with high uptime and very low maintenance.
How Do UV LED Emitters Influence the Curing Process?
LED emitters determine the fundamental energy output for curing by converting electrical current directly into ultraviolet light. You will find that the design of the LED array—specifically the density and arrangement of the individual diodes—affects the intensity of the light hitting your product. These emitters are the heart of the technology, providing the specific spectral energy required to trigger the chemical reaction in your photo-curable materials.
The layout of these emitters is often referred to as the "array" or "COB" (Chip on Board) design. If the emitters are spaced too far apart, you might experience "striping" or uneven curing on your parts. If they are packed tightly together, the intensity (irradiance) increases, allowing you to run your conveyor belt at much higher speeds. Your choice of emitter quality also dictates how long the system will last before the light output begins to degrade. High-quality emitters stay stable for tens of thousands of hours, ensuring that your last part of the year is cured exactly like the first.
How Does Optics and Light Distribution Affect Cure Uniformity?
Optics and light distribution determine how evenly cure energy reaches surfaces by using lenses or reflectors to focus the UV beam. You need high-quality optics to ensure that the light intensity is consistent across the entire width of your product, preventing "hot spots" or uncured edges. Proper distribution is vital when you are working with wide substrates or complex 3D parts, as it ensures that every area receives the same dose of energy for a reliable and repeatable finish.
Different lenses serve different purposes in your workflow. For example, a "wide-angle" lens might be used to cover a large area at a close distance, while a "collimating" lens is used to keep the light beam narrow and intense over a longer distance. If your lamp head is mounted far from your product, the optics must be powerful enough to keep the light from scattering. Without good optics, much of the UV energy you pay for is wasted as it bounces off the machine walls instead of hitting your product.
What Role Does Power Supply and Control Electronics Play in Cure Performance?
Power supply and control electronics influence energy stability and curing repeatability by managing the electrical flow to the LED emitters. You rely on these components to maintain a steady light intensity, even when your facility's incoming power fluctuates. Advanced control electronics also allow you to dim the light or pulse the energy, which gives you the flexibility to match your curing output to different line speeds and material requirements.
The "drivers" inside the power supply are particularly important for your operation. They ensure that the LEDs receive a clean, constant current, which prevents flickering. Flickering is a major cause of poor adhesion or tacky spots, especially at high line speeds. Modern electronics also include sensors that monitor the health of the system. If a power surge occurs or a component starts to fail, the control electronics can safely shut down the system to prevent a fire or permanent damage to the expensive LED arrays.
How Does Wavelength Selection Influence Material Compatibility and Cure Depth?
Wavelength selection determines material compatibility and cure depth by matching the light's spectral peak to the specific photoinitiators in your ink or adhesive. You must choose a wavelength, such as 365nm or 395nm, that can penetrate through the entire thickness of your coating. If the wavelength is not correctly matched to the material chemistry, you may find that the surface feels dry while the bottom layer remains liquid, leading to a failure in bond strength.
Shorter wavelengths (365nm) are often used for surface curing because they provide a high-energy "hit" that creates a hard, scratch-resistant top layer. Longer wavelengths (395nm or 405nm) have a greater ability to travel through opaque or thick coatings, reaching all the way to the substrate. In many advanced manufacturing lines, you might see a system that uses a combination of both wavelengths. This ensure that you get a hard surface and a deep, structural bond at the same time.
Why Are Thermal Management and Heat Dissipation Important in UV LED Curing?
Thermal management affects both performance and component longevity by removing the internal heat generated by the LED diodes during operation. You need effective heat sinks, fans, or water-cooling systems to keep the emitters at a stable temperature, which prevents the light output from drifting over time. Proper heat dissipation is a key factor in system reliability, as it protects the delicate electronics from damage and ensures your curing results remain consistent throughout long production shifts.
If the LEDs get too hot, their efficiency drops. This means you get less light for every watt of power you use. Furthermore, extreme heat can cause the diodes to fail prematurely, leading to expensive repairs. You will usually choose between "air-cooled" and "water-cooled" systems. Air cooling is simple and uses fans to blow air over fins. Water cooling uses a chiller and is necessary for high-power systems where the lamps are small and the power is very high. Keeping the system cool is the best way to protect your investment for the long run.
How Do UV LED Curing System Interfaces and Controls Affect Operation?
System interfaces and controls shape how operators manage curing by providing a way to monitor performance and adjust settings in real-time. You use these interfaces to set the light intensity, track the running hours of the equipment, and receive alerts if a component fails. Modern controls often include automation features that link the light output directly to your conveyor speed, making the entire process easier to manage and reducing the risk of human error.
Many systems now allow for "remote monitoring" via a PLC or computer network. This means you can see exactly how the curing line is performing from your office. You can track energy use and predict when maintenance is needed before a breakdown happens. This digital connection turns your curing equipment into a smart tool that works with your other factory machines. It helps you maintain a high standard of quality without needing to constantly manually check the machine.
What Are the Key Takeaways on How Components Affect Cure?
Cure quality is the direct result of how your emitters, optics, and thermal controls work as a unified system. You should prioritize high-quality components that offer stability and precise wavelength matching for your specific materials.
- LED emitters provide the core energy needed for the chemical bond.
- Optics ensure that the light is spread evenly across your entire part.
- Power controls keep the light intensity steady for repeatable results.
- Thermal management protects your equipment and prevents output drift.
- User interfaces give you the data needed to maintain full process control.
How Does UV LED Curing Work Across Different Equipment Types?
The way a component behaves can change depending on the machine it is mounted in. You can explore the core behavior of this tech by visiting our UV LED curing and how it works pages. For a technical deep dive into the engineering behind these parts, check our UV LED curing technology section.
What Are the Typical Applications for UV LED Curing Technology?
Different industries prioritize different components; for example, printing needs wide optics, while electronics need high-intensity emitters. You can see how these parts are applied in various sectors on our UV LED curing applications page. This helps you understand which components matter most for your specific production goals.
What Are the Benefits of UV LED Curing Compared to Traditional UV Sources?
The design of LED components offers several advantages over old lamp styles, such as instant-start power and lower heat transfer. You can find a full list of these gains on our UV LED curing benefits page. These benefits are directly linked to the solid-state nature of the components used in modern systems.
What Safety Considerations Apply to UV LED Curing Equipment?
While LED components are safer than mercury bulbs, you still need to manage high-intensity UV light. We provide a guide on UV LED curing safety that explains how to use shielding and PPE with these specific equipment types. Understanding component behavior helps you build a more secure production line.
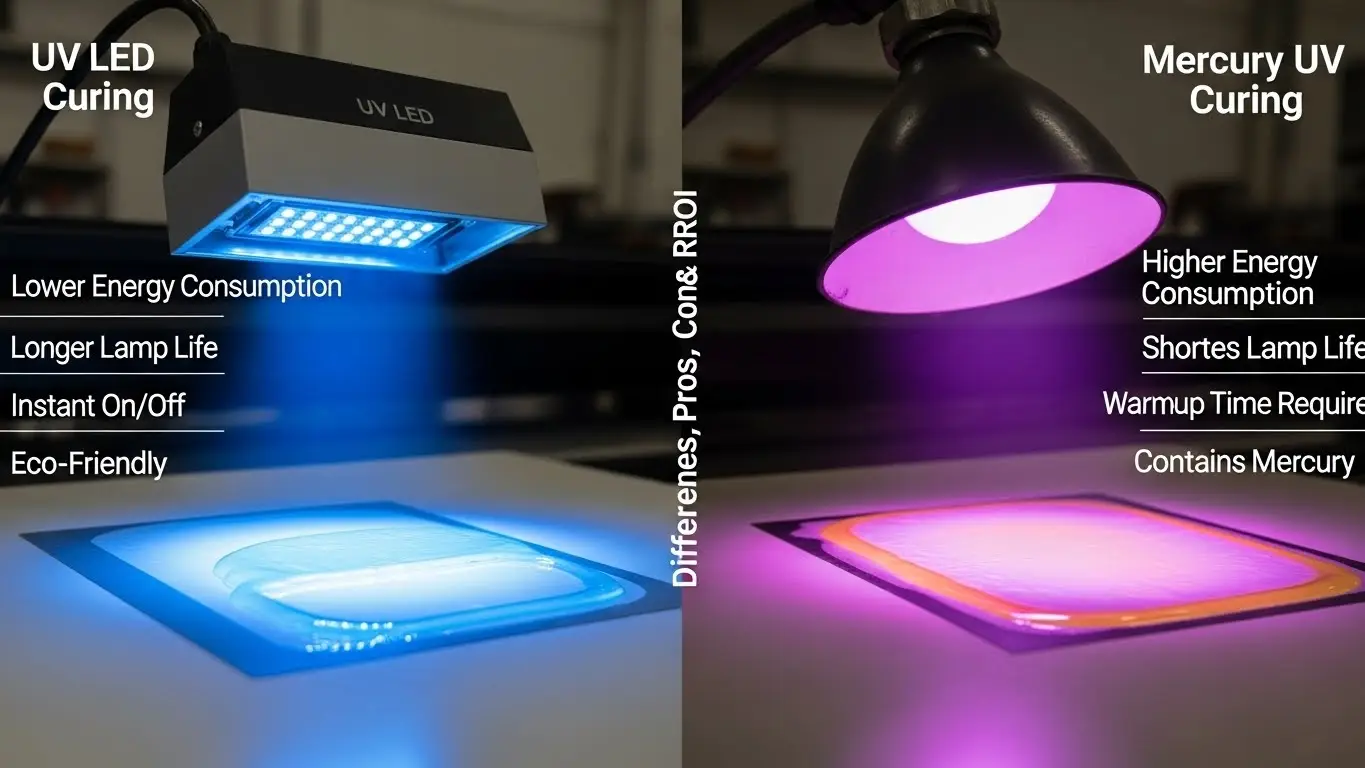
How Does UV LED Curing Technology Compare to Mercury UV Curing?
There are major differences in how these two technologies generate light and handle heat. You can see a component-level breakdown at UV LED vs mercury UV curing. This comparison helps you see why the modern LED approach is often more reliable and easier to maintain for your shop.
What Checklist Helps You Evaluate UV LED Curing Components?
When you are ready to buy, you need a way to compare emitters, optics, and power supplies fairly. We have created a guide to choose a UV LED curing system that provides a structured path for technical evaluation. This checklist ensures you don't overlook critical details like thermal management or interface compatibility.
What Light Characteristics Should You Consider in UV LED Curing Technology?
The physical parts of your system create the light profile that hits your product. You should research the specific UV LED curing light characteristics, such as peak irradiance and dosage, to ensure they match your process needs. This technical alignment is what prevents curing failures and improves your final quality.
How Do UV LED Curing System Configurations Influence Component Behavior?
The way you arrange your lamp heads and power units affects how well they can dissipate heat and deliver light. You can browse various UV LED curing equipment setups to see how different configurations impact component performance. This helps you visualize how the technology will sit on your conveyor belt or robotic arm.
Final Thoughts
Selecting a system based on its internal components ensures that you are building a process on a foundation of reliability rather than just a product name. As the industrial world moves toward higher precision and lower energy use, the quality of your emitters and thermal management will be what keeps you competitive. By focusing on how these individual parts affect your cure, you gain the knowledge needed to maintain a high-speed, high-quality production line for years to come. The right technology does not just light up your product; it secures your entire manufacturing reputation through consistent, high-performance results.