LED Curing Light vs UV Lamp: Practical Differences in Production
Selecting the right ultraviolet source for your shop floor requires you to look past technical specs and focus on how the equipment behaves during an active shift. You will find that moving from a bulb-based system to a diode-based system changes how you handle parts, manage your time, and organize your workflow. This guide examines the daily operational realities of using an LED curing light vs UV lamp in a high-volume production environment. By understanding these practical differences, you can better plan your facility upgrades and ensure your production outcomes meet your quality and speed requirements.
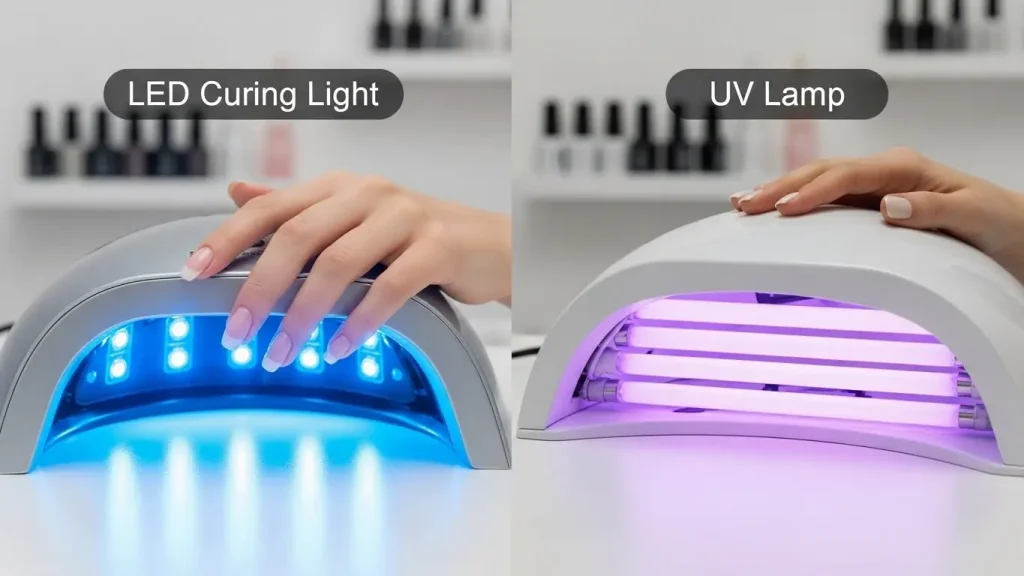

What Are the Practical Production Differences Between LED Curing Lights and UV Lamps?
LED curing lights and traditional UV lamps behave differently in production due to distinct energy delivery, temperature, and control characteristics. You will notice that LED systems allow for instant-start operation, meaning you do not have to wait for the equipment to warm up before starting your line. Traditional UV lamps, however, offer a broader spectral output that can handle a wider variety of standard inks without needing specialized chemical formulations. These differences dictate how often your team stops the line and how much energy your facility consumes during idle periods.
How Does Heat Generation Compare Between LED Curing Lights and UV Lamps?
LED curing lights typically run cooler than traditional mercury UV lamps, which influences part temperature and fixture design. You can process heat-sensitive plastics and thin films under an LED source without the risk of the material warping or melting. In contrast, traditional mercury lamps emit significant infrared energy, often requiring you to install extra cooling fans or chilled rollers to prevent your products from being damaged by excessive heat. This lower thermal profile also makes the workspace more comfortable for your operators and reduces the load on your building's air conditioning system.
How Do Operational Constraints Differ in Production Environments?
Operational constraints such as dwell time, line speed, and material flow differ between LED and UV lamp curing in production. You must account for the fact that LEDs provide a narrow, high-intensity light that may require you to adjust your conveyor speed to ensure the material receives the correct total energy dose. Because traditional lamps provide a broader spectrum, they may be more forgiving of slight variations in line speed, whereas LED systems require a more precise match between the light intensity and the time the part spends under the lamp head.
What Material or Curing Limitations Should Production Teams Be Aware Of?
Both LED curing lights and traditional UV lamps have material and penetration limitations that production engineers need to consider. You may find that certain thick or opaque coatings are difficult for the narrow wavelength of an LED to penetrate fully, potentially leaving the bottom layer uncured. Traditional UV lamps can sometimes struggle with surface tackiness if the intensity is not high enough, but their broad light range generally provides better "through-cure" for complex, multi-layered chemical recipes that have not been optimized for LED.
How Do Retrofit Considerations Affect Production Transition Plans?
Retrofit considerations, including equipment layout and process validation, affect how production lines transition from UV lamps to LED curing lights. You need to evaluate if your current machine frames can support the more compact LED lamp heads and if your electrical panels can handle the specific power requirements of LED drivers. A transition plan must also include a validation phase where you test your existing materials under the new light source to ensure that adhesion and hardness levels remain consistent with your previous production standards.
How Should Production Teams Evaluate LED vs UV Lamps in Their Specific Use Case?
Evaluating LED versus UV lamps should be based on specific production requirements, including materials, throughput, and constraints. You should start by auditing your most common substrates to see if they are heat-sensitive, as this often makes LED the logical choice. Additionally, you must weigh the upfront equipment cost against the long-term savings in bulb replacements and electricity.
- Substrate Sensitivity: Choose LED if your parts are prone to thermal distortion.
- Production Volume: Consider LED for high-volume lines where energy efficiency and long lamp life provide the fastest return.
- Material Flexibility: Stay with or choose traditional UV lamps if you need to run a wide variety of legacy coatings that are not LED-optimised.
- Uptime Requirements: Opt for LED if your process requires frequent starts and stops throughout the day.
What Are the Key Takeaways on Practical Differences for Production?
The practical choice between these light sources depends on whether your production goals prioritize spectral versatility or operational efficiency. You get a more stable, cooler, and energy-efficient process with LED, while traditional lamps offer a broader chemical compatibility that can be simpler for diverse shops.
- LEDs provide instant-on capability and much lower heat transfer to parts.
- Traditional lamps offer a broad light spectrum for easier material compatibility.
- Transitioning to LED requires careful material validation and equipment layout planning.
- Long-term maintenance is significantly lower with LED-based systems.
How Do LED and Traditional UV Curing Technologies Compare Fundamentally?
To understand the core physics behind these production differences, you can read our technical breakdown of UV LED vs mercury UV curing. This explains the spectral differences that drive the heat and speed variations you see on your shop floor.
How Does Temperature Behavior Differ Between LED and UV in Production?
Managing the heat on your production line is vital for part quality. You can find detailed data on UV LED curing temperature to see how much cooler your substrates could be. This is especially important for maintaining the integrity of sensitive materials.
What Material Limitations Are Typical With LED Curing in Production Settings?
Before you switch, you should be aware of the limitations of UV LED curing regarding penetration and surface tack. Knowing these constraints helps you avoid production errors and ensure every part is fully cured.
What Challenges Are Involved When Retrofitting from UV Lamps to LED Lights?
Planning an upgrade requires a look at both hardware and workflow. You can find guidance on the common hurdles in our retrofit mercury to UV LED guide. This covers the practical steps needed to modernize your current machinery.
How Do LED or UV Curing Lamps Affect Throughput and Line Speed?
Your throughput is directly tied to the "dosage" of UV light your parts receive. LEDs allow for higher peak intensity, which can often support faster line speeds if your material is properly formulated. However, traditional lamps may be more stable if your line speed fluctuates, as their broad spectrum provides a more generalized cure.
What Safety Considerations Should Be Accounted for in Production?
While LED lights remove the risk of mercury spills and ozone gas, they still produce high-intensity UV energy. You must ensure that your production line has proper light shielding and that your operators have access to UV-rated personal protective equipment.
How Should ROI Be Considered When Changing Curing Systems on the Production Floor?
The return on investment for changing your curing system comes from reduced electricity bills, fewer bulb changes, and lower scrap rates. You should calculate your total cost of ownership over a three-to-five-year period to see the true financial benefit of switching to a solid-state LED system.
What Questions Should You Ask to Assess LED vs UV Lamps for Your Production Process?
You should start by asking your ink supplier if they offer a dual-cure or LED-specific version of your current coatings. You also need to ask your maintenance team about the current downtime caused by mercury bulb failures. These answers will help you build a clear case for which technology fits your specific production environment.
Final Thoughts
Finalizing your decision on curing equipment requires a balance between current production demands and future facility goals. While traditional UV lamps provide a reliable and familiar broad-spectrum cure, the practical advantages of LED curing lights—such as low heat, instant power, and high reliability—are making them the new standard for modern manufacturing. By focusing on the specific needs of your materials and the constraints of your shop floor, you can select a system that improves your quality and reduces your daily operating costs. The best choice is the one that allows your production line to run as smoothly and efficiently as possible.